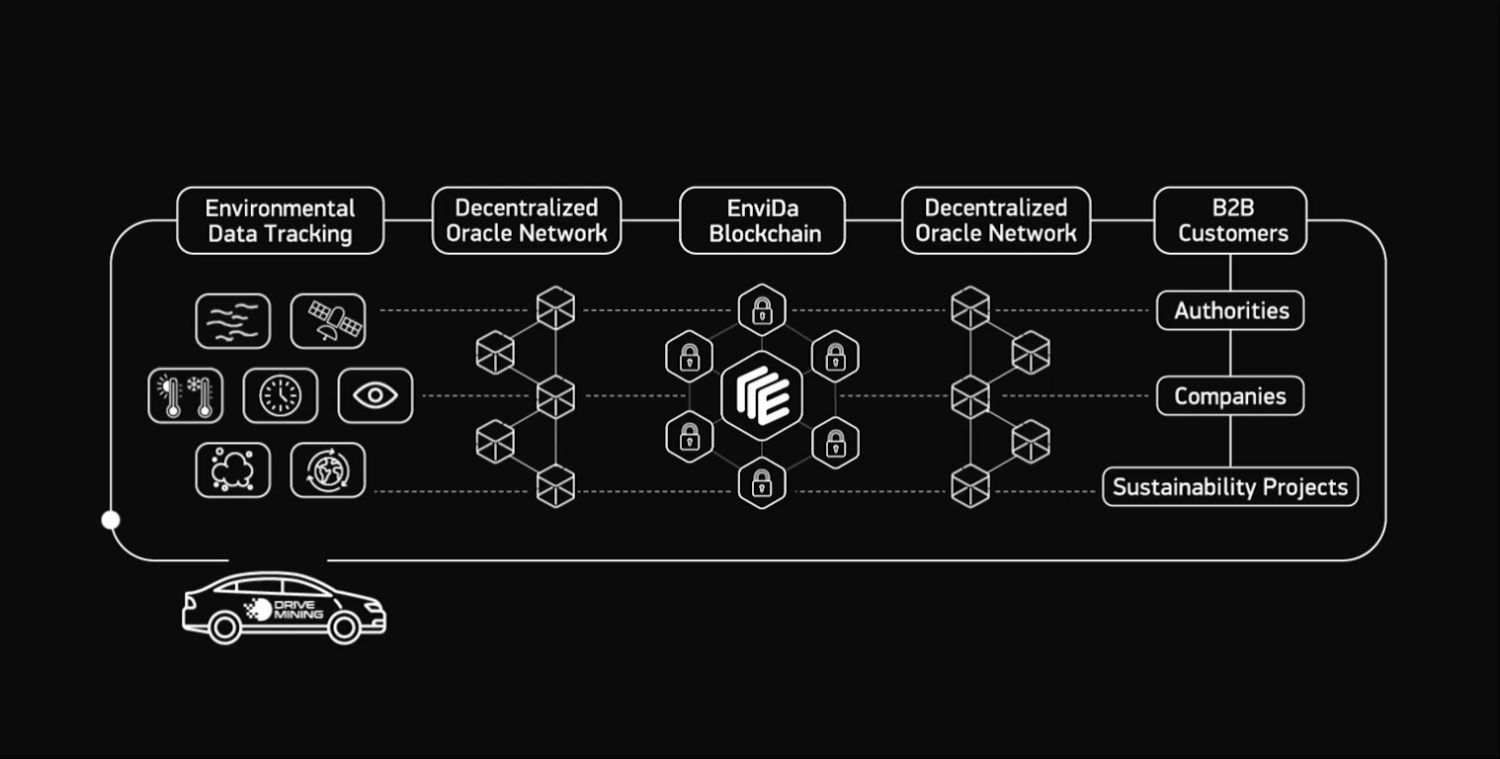
EnviDa-Token FAQ
A cryptocurrency distributed by your mobile operator and accepted everywhere.
What does cryptocurrency mean in general?
A cryptocurrency (crypto money) is a digital currency with a cryptographically secured and decentralized payment system. Unlike traditional fiat money, such as dollars or euros, a cryptocurrency exists only in its digital form and managed by a decentralized peer-2-peer (“P2P”) network. The technical implementation of digital currencies is based on the so-called blockchain. Cryptocurrencies are intended to enable users to make cashless payments. In direct comparison to the classic currency, no banknotes or coins are used for a cryptocurrency. Everything runs completely digital. The inventor’s goal was to create a currency that is free and not controlled by a central body, as it usually is.
What is Crypto Mining?
The process of mining is described in more detail below, using Bitcoins as an example: First, the term blockchain must be discussed with more details. A blockchain is a “distributed ledger” (literally translated: “distributed account book”), on which the virtual currency Bitcoin is based. A distributed ledger is a public, decentralized account book. In the area of virtual currencies, this is used to record transactions between individual users without the need to set up a central office to check each individual transaction. Mining, in very general terms, is a legitimization process in the Bitcoin network. It is the process of securing and verifying Bitcoin transactions. The Bitcoin transactions first wait on the blockchain to be confirmed. Only after successful confirmation, the individual Bitcoin transactions can be executed. In the process, all computers working in the Bitcoin network check whether the pending transactions contradict the previous transaction history. For this purpose, the account books stored decentrally on all these computers are compared with the transaction history. Once a majority of the computers have determined the transactions to be free of contradictions, they are confirmed. In the Bitcoin network, there is a competition between the participating computers, as the operator of the fastest computer receives bitcoins in return for its activity. In a similar way to gold mining, the entire legitimization process is called “mining” and the operators of the computers are called “miners.
What is the blockchain?
Basically, blockchains are nothing more than databases – storage for huge amounts of data. The main difference to, for example, a Microsoft Access database: the Access database exists locally as a single file, the blockchain database is distributed in a network. This is a completely normal peer-to-peer network. In principle, the blockchain is a shared account book that everyone can check, but no individual can control.
What is the hash power?
The hash power is the computing power used to solve the computational tasks in the blockchain and to confirm the transactions. For this process, you receive a reward in the form of coins.
What is a Wallet?
A wallet is the place where you can store your cryptocurrencies. You can have your own wallet on your computer or smartphone or there is also the possibility of an online wallet.
How to get a wallet?
We recommend MetaMask here. MetaMask is a crypto wallet that supports all types of Ethereum-based tokens. MetaMask can serve as a regular crypto wallet, but its real strength lies in its seamless connectivity to smart contracts and decentralized applications. If you need any help, we are happy to assist. MetaMask link: metamask.io
What is Blocktime?
The blocktime represents the fixed period of time within which transactions are checked or verified by the miners in order to be able to insert them into an existing block.
What is a mining pool?
In the context of cryptocurrency mining, a mining pool is the pooling of resources by miners, who share their processing power over a network in order to receive rewards according to the amount of work they have contributed to the likelihood of finding a block, to be divided equally. A “share” is awarded to mining pool members who provide valid proof of share. Pool mining began when the difficulty for individual mining became so great that it could take centuries for slower miners to build a block. The solution to this problem was, miners to pool their resources together so that they could generate blocks more quickly and therefore earn a portion of the block reward consistently rather than randomly every few years.
What are miners?
Miners control the network, keep it stable and verify new transactions on the network. So, in a nutshell, they check if the new transactions are okay and follow the protocol. If everything is okay, they have the ability to append a new block to the blockchain for all eternity. Since the overall state in a decentralized blockchain is no longer managed by central entities, it needs the miners to do it for us. This keeps the whole thing decentralized. The more miners there are, the more stable a blockchain network becomes and the less vulnerable it is against a 51% attack or takeover of the blockchain.
What is the Difficulty?
The difficulty is the degree of difficulty in a blockchain network to find a new block. More miners in a blockchain network mean, higher total computing power in a network. So that now by the increase of the computing power in the network, not more blocks in a shorter time can be found, the blockchain protocol automatically adjusts the difficulty. This ensures, for example, that in the Bitcoin blockchain, a block is “found” every 10 minutes, and not, for example, in 3 or 6 minutes. Since with the Bitcoin network, every 2016th block or every two weeks, the Difficulty is adjusted, one could briefly, if the computational power changes, you could make more profit from mining. However, since the Difficulty in the blockchain network is variable, it is adjusted depending on the period set, according to the computing power in the entire network.
What is meant by Proof-of-Work?
The proof-of-work mechanism is a form of the so-called consensus mechanism to reach a consensus in the network and to agree on an identical version of the blockchain. Performing a proof-of-work mechanism or calculating the results is referred to as “mining” in the context of blockchains as “mining.” In this process, the miners try to find a result with certain properties by performing billions of arithmetic operations. Once you have hit such a result, you are remunerated. The basic principle of proof-of-work is based on the idea that miners must prove to the network that they have expended a certain amount of effort. Proof-of-work mechanisms were also used in the past for sending e-mails, to prevent spam. In order to send an email, the sender had to perform additional computations, in simple terms. to be performed. Since the machines were limited in their computing capacity, it has been necessary to make large investments to perform the calculations and send the e-mails. to perform the calculations and ultimately send e-mails. This meant that the cost of sending e-mails should be high enough that it is no longer worthwhile for spammers to send them. Because the recipient of an e-mail could check in a simple way whether the calculations were carried out correctly, while the sender had to invest were associated with a certain effort for the sender.
Stay in Touch
For more information about us, you can browse DriveMining and follow our social media accounts.
Developed & Regulated in